
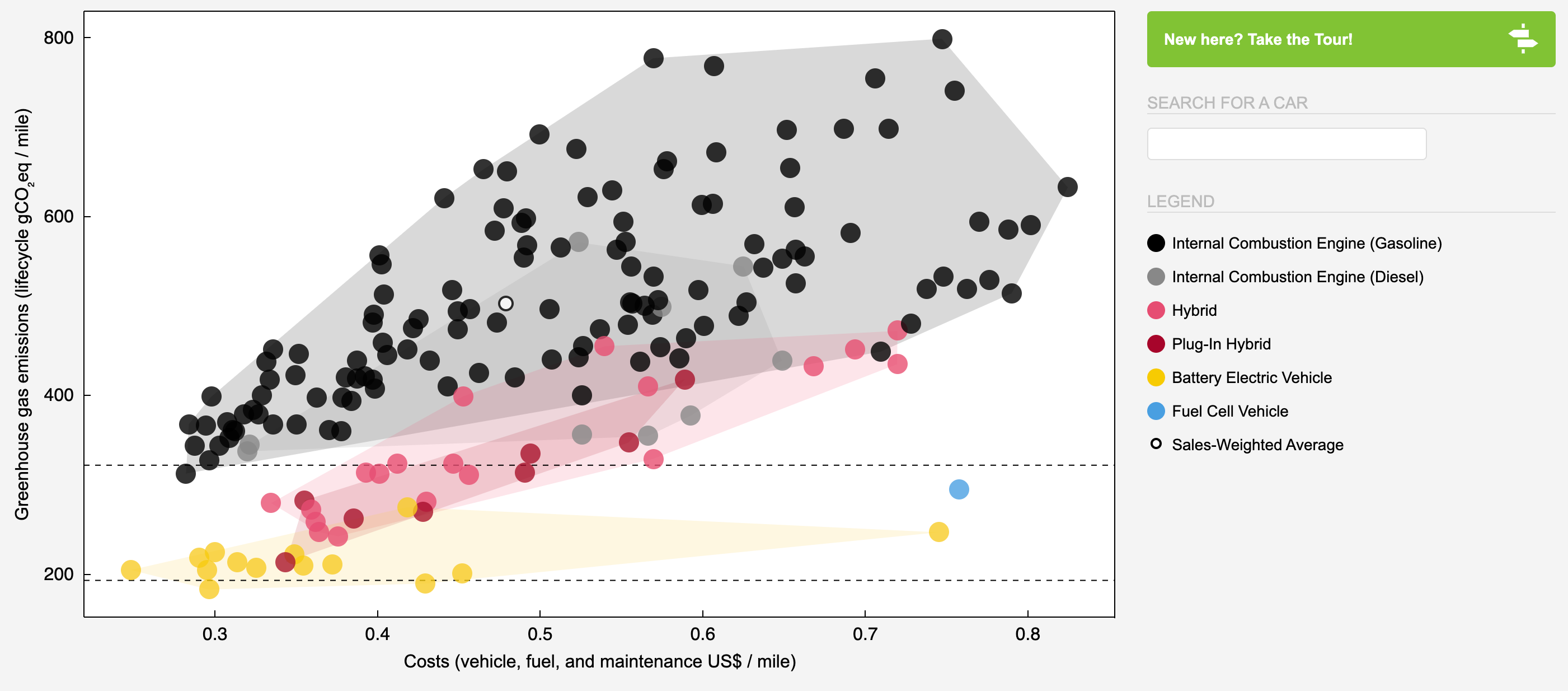
The Grid Gets Greener: EVs Prove Twice as Carbon-Efficient as Hybrids
The UK's electrical grid is becoming increasingly green, directly benefiting electric vehicle (EV) environmental impact. Here's a detailed analysis of how EVs compare to traditional vehicles in terms of emissions.

Two wind turbines against sky
Grid Carbon Intensity Improvements:
- 2018: 247.99 g/kWh
- 2019: 212.71 g/kWh (14% reduction)
- Continued decrease due to reduced coal usage and increased renewable energy, particularly wind power
EV vs. Hybrid Emissions Comparison:
- Average EV (300Wh/mile efficiency): Approximately 64g CO2/km using 2019 grid figures
- Toyota Yaris 1.5L Hybrid: 87g CO2/km (NEDC)
- Standard Toyota Yaris 1.5L: 113g CO2/km
Key Findings:
- EVs produce roughly half the emissions of the most efficient hybrid vehicles
- Grid improvements alone reduced EV emissions by ~50% over five years
- EVs become cleaner automatically as the grid gets greener
- Even accounting for battery manufacturing, EVs have lower lifetime emissions
Carbon intensity chart UK grid power
Additional Considerations:
- These calculations don't include emissions from fuel extraction, processing, and transportation for traditional vehicles
- While EV manufacturing currently has a higher carbon footprint, manufacturers like VW are moving toward carbon-neutral production
- Complete lifecycle analysis shows EVs have significantly lower environmental impact than conventional vehicles
The data clearly shows that EVs are substantially more environmentally friendly than hybrid or traditional vehicles, with this advantage increasing yearly as the grid continues to incorporate more renewable energy sources.
Related Articles

New Audi A7 and RS7 spotted: A6 replacement coming in 2025

